Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
- Adopting healthy habits at any age boosts longevity: A 20-year study of over 49,000 Japanese adults found that even middle-aged and older individuals (ages 40–80) can add up to six years to their life by adopting simple, modifiable lifestyle habits.
- Key longevity-boosting habits include: Eating more fruits and fish, maintaining a healthy BMI, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol, and getting 5.5 to 7.4 hours of sleep each night. Each habit added at least half a year to life expectancy.
- Non-smoking and moderate alcohol intake had the biggest impact: Never smoking added nearly 4 years to life expectancy, while drinking less than 46 grams of alcohol per day added up to 4.9 years for women and 1.9 years for men.
- Healthy choices pay off—even in a long-living population: Despite Japan already having one of the highest life expectancies in the world, the study showed that adopting more healthy behaviors can still yield meaningful lifespan gains, proving it’s never too late to start.
Healthy Habits Can Add Up to Six Extra Years of Life — Even If You Start Later
Researchers followed 49,021 men and women between the ages of 40 and 80 for two decades, focusing on how modifiable lifestyle habits affected life expectancy. Japan, with one of the highest life expectancies in the world—averaging 87.7 years for women and 81.6 years for men as of 2020—served as the study setting. The research sought to determine whether individuals in a country already known for long lives could still benefit from healthy changes. The answer was a resounding yes. The study analyzed several modifiable health habits, including:- Regular consumption of fruits and fish
- Maintaining a healthy body mass index (BMI)
- Routine physical activity
- Avoiding smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Getting adequate sleep
- Never smoking yielded the largest gains—adding 3.8 years for men and 3.7 years for women.
- Drinking less than 46 grams of alcohol daily added 1.9 years for men and an impressive 4.9 years for women.
- Maintaining a healthy body composition added 1.3 years for men and 1.7 years for women.
- Sleeping between 5.5 to 7.4 hours nightly added 1.4 years for men and 1.6 years for women.
A scientific exploration of love’s healing power: “Love and Survival” by Dr. Dean Ornish
By Kevin Hughes // Share
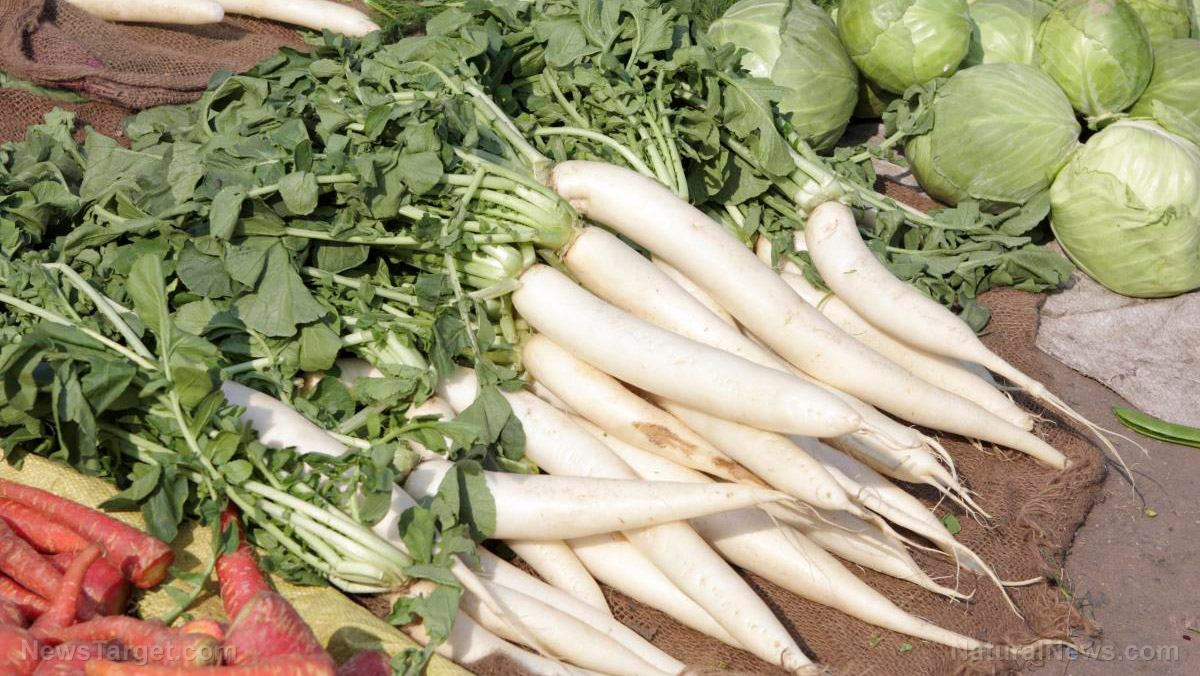
Radish: A crunchy root vegetable to boost your nutrition
By Laura Harris // Share
“Sinus Survival” sheds light on the crucial role of sinuses in our health
By Kevin Hughes // Share
Aging is inevitable but suffering is optional
By Lance D Johnson // Share
The power of sleep: How rest rewires your brain for better decisions
By Ava Grace // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share